FDM (Fused Deposition Modelling)
Ideal for prototyping and functional parts using thermoplastics.
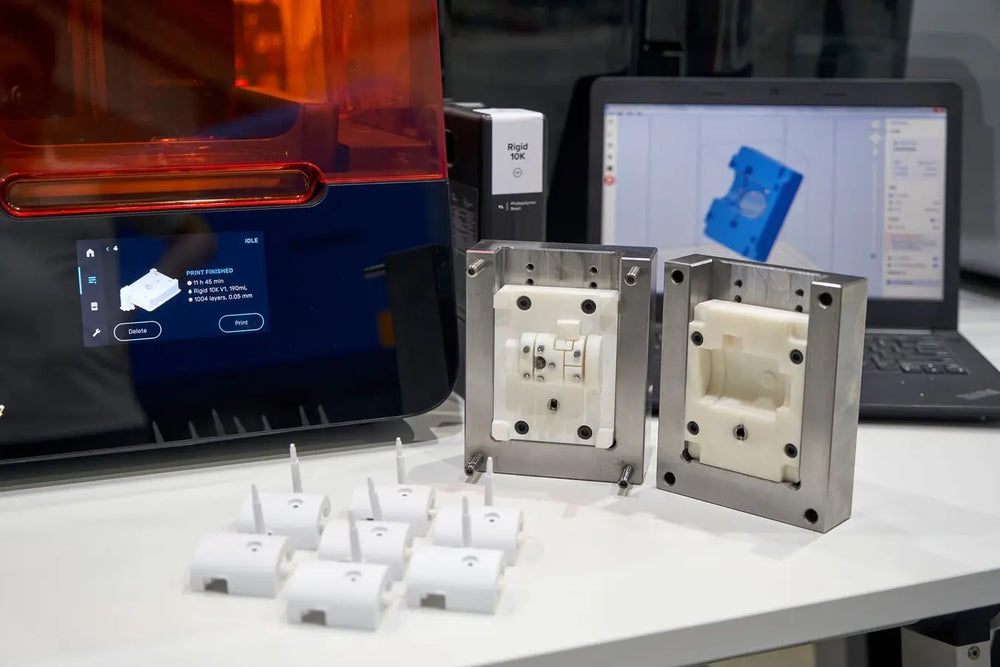

Ideal for prototyping and functional parts using thermoplastics.
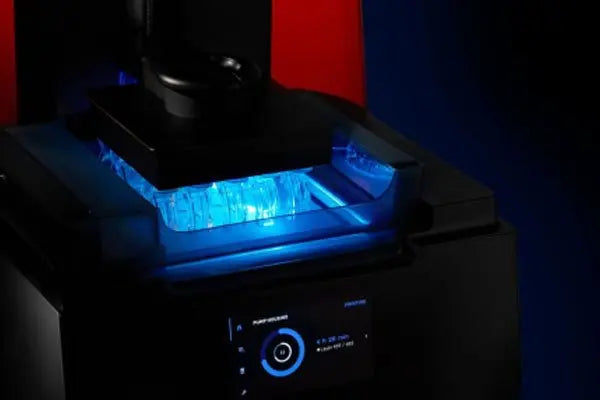

High-detail resin printing for precision components.
Powder-based methods used for strong, durableindustrial parts.

Metal 3D printing for aerospace,medical, and automotive applications.